Key takeaways:
Benadryl (diphenhydramine) and Claritin (loratadine) are over-the-counter (OTC) antihistamines. They can both help relieve allergy symptoms. But Benadryl can also help with occasional sleep difficulties and motion sickness.
Claritin lasts longer in your body than Benadryl, so you don’t need to take it as often. Claritin also has a lower risk of side effects, such as drowsiness and dizziness.
Benadryl and Claritin are available OTC as brand-name medications. But you can also find them as lower-cost generics. GoodRx can help make your medication more affordable.
Save on related medications
If allergies have you sneezing nonstop, you’re probably looking for relief. But with all the allergy medications available, it can be hard to pick one. Antihistamines are a common choice because they start working fast and can be taken daily to help prevent symptoms.
Benadryl (diphenhydramine) and Claritin (loratadine) are popular antihistamines. They’re both readily available over the counter (OTC) and offer doses for adults and kids. But how do you choose between these antihistamines? Below, we dive into seven differences to keep in mind when comparing Benadryl versus Claritin.
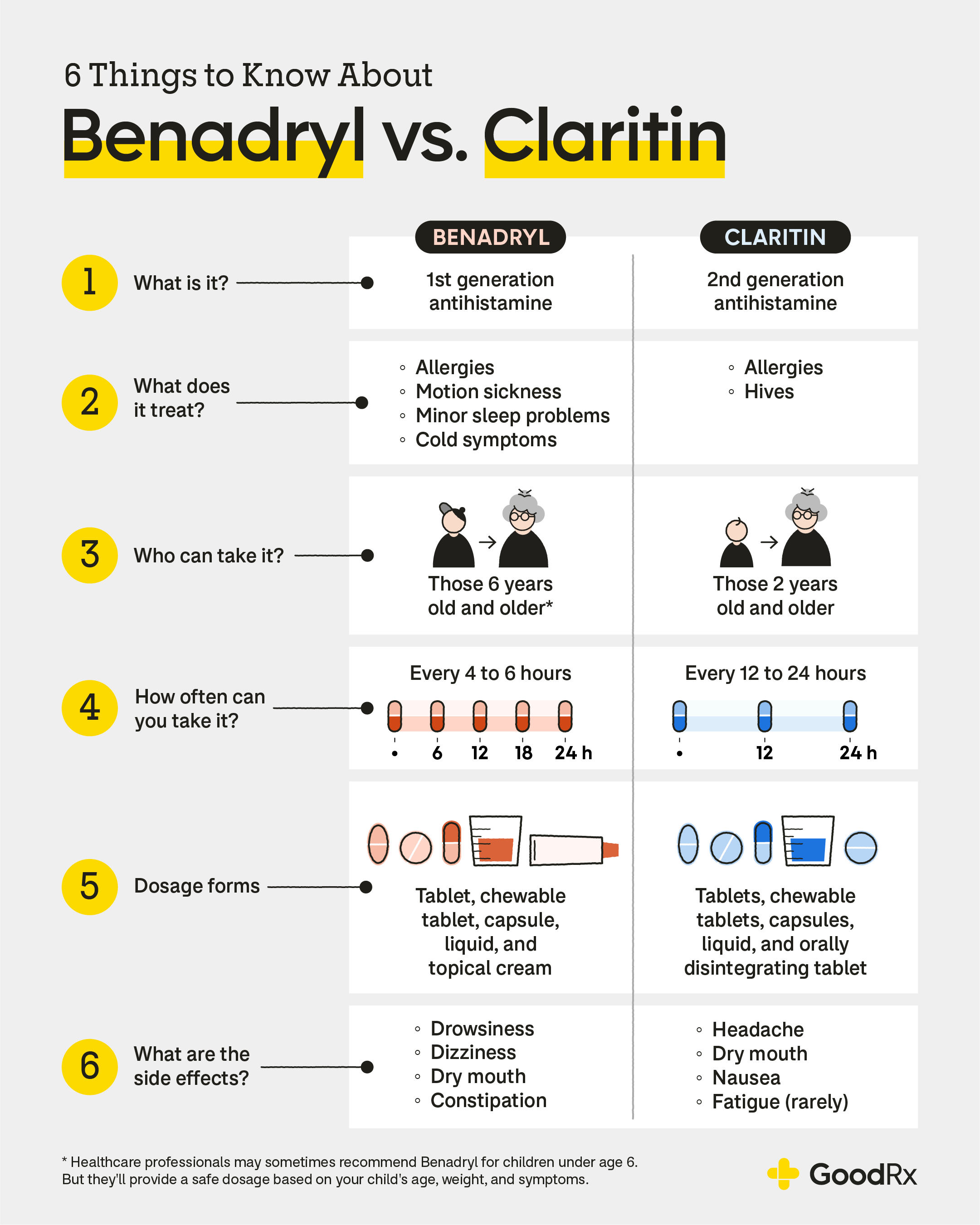
1. Claritin lasts longer than Benadryl
If you’re looking for relief that lasts all day, you might prefer Claritin over Benadryl. Its effects last longer in the body. Claritin comes in 12- and 24-hour versions. So you’ll need to take it once or twice a day. In comparison, you may need to take Benadryl every 4 to 6 hours for continued symptom relief.
Search and compare options
2. Claritin is considered nondrowsy
It’s no secret that Benadryl causes drowsiness. But Claritin usually doesn’t. So if you’re looking for an allergy medication you can take anytime of day, Claritin might be a better option.
Benadryl causes drowsiness because it reaches the brain more easily than Claritin. That doesn’t mean it’s impossible for Claritin to make you sleepy. Drowsiness can happen with any antihistamine. But the risk is much lower with Claritin than Benadryl.
It’s a good idea to take your first dose of Claritin when you don’t have to drive or perform other activities that require focus. That way, if it does make you sleepy, you can rest. And if Claritin does cause drowsiness for you, plan to take your doses in the evening. Fatigue from the medication will likely wear off by the time you wake up the next morning.
3. Benadryl can also be used for occasional sleep troubles
Many people use Benadryl’s drowsy side effect to their advantage if they’re having trouble sleeping. In fact, diphenhydramine (Benadryl’s active ingredient) is included in popular OTC sleep medications.
Examples include:
Comparing options: Learn about the different types of allergy medications so you can choose the right one for you.
What to expect: Drowsiness and headaches are some of the notable antihistamine side effects.
More than medication: Three people share the daily lifestyle changes that have been effective at reducing their allergy symptoms.
Because Claritin doesn’t usually cause drowsiness, it’s not helpful for sleep problems. Even though Benadryl is safe for many people to use for sleep, it’s not a good long-term solution. Don’t take Benadryl for trouble sleeping for more than 2 weeks in a row unless a healthcare professional tells you to.
If you’re taking Benadryl for sleep, keep in mind that the dosage is different from what’s recommended for allergy relief. For sleep, the typical dosage is 50 mg taken about 30 minutes before bedtime. For allergy symptoms, it’s 25 mg to 50 mg every 4 to 6 hours as needed for people ages 12 and older. The Benadryl dosage for allergies is lower for children under 12.
4. Benadryl can be used for motion sickness
Benadryl can also help treat and prevent motion sickness. This is because it can block chemicals in your brain that cause this symptom. Claritin doesn’t work for motion sickness because it doesn’t reach the brain as easily.
Benadryl dosages for motion sickness are different from those for allergy relief. It works best if you take 25 mg to 50 mg about 30 to 60 minutes before the triggering activity, such as a car ride. Depending on how long the activity lasts, you may need to take another dose 4 to 6 hours later.
5. Claritin is safer for older adults
Older adults tend to be more sensitive to many of Benadryl’s side effects, including:
Drowsiness
Dizziness
A higher risk of falls
Confusion
Trouble urinating
Constipation
Because of this, experts recommend avoiding Benadryl if you’re age 65 or older. Nondrowsy antihistamines, such as Claritin, are a safer choice. Claritin has a much lower risk of serious side effects.
Good to know: If you have a history of allergic reactions, ask your healthcare team which medications to keep on hand. For mild reactions, some healthcare professionals may recommend taking Benadryl instead of Claritin. But no antihistamine should be used to treat severe allergic reactions, such as anaphylaxis. You should use epinephrine (EpiPen, Auvi-Q, neffy) and seek emergency medical care in this situation.
6. Claritin has dosage information for kids as young as 2 years old
If you put the OTC labels for Benadryl and Claritin side by side, you’ll notice a difference in age ranges. Both have children’s versions available, but the minimum ages listed are different.
Benadryl’s label has dosage information only for children ages 6 and older. For children under 6, you’ll see wording such as “don’t use without asking a healthcare professional.” This is because Benadryl dosages for young children should be determined using their body weight. A pediatrician is the best person to ask for a safe Benadryl dosage.
On the other hand, the label for Children’s Claritin has dosage information for kids as young as age 2. It can be safely given to most children this age. Just make sure the product you have lists your child’s age range on it. Adult Claritin dosages are higher than dosages for young children.
7. Benadryl also comes available as a cream
Most people think of pills or liquids when they hear the names Benadryl and Claritin. But Benadryl also comes as a topical cream and gel that you can apply to your skin. This can be helpful for minor skin reactions, such as bugbites or mild burns. Keep in mind that Benadryl cream doesn’t help with other allergy symptoms, such as sneezing or watery eyes.
Claritin doesn’t come in a topical form.
Can you take both Benadryl and Claritin?
In most cases, you shouldn’t take both Benadryl and Claritin. This raises your risk of side effects without providing extra allergy relief. You’re more likely to experience drowsiness and dizziness if you take both. And in severe cases, taking too many antihistamines at once can cause dangerous overdose symptoms.
If Benadryl or Claritin isn’t working well enough on its own, speak with your primary care provider or a pharmacist. They can recommend a safe combination of allergy medications for you to try.
How do you choose between Benadryl and Claritin?
When it comes to seasonal allergy relief, most people are better off trying Claritin first. All oral antihistamines work similarly well for symptoms like sneezing, runny nose, and watery eyes. But Claritin has a much lower risk of side effects than Benadryl, particularly if you’re age 65 or older.
If allergy symptoms are keeping you up at night, then Benadryl might be more helpful. Taking a dose at night might help with both allergies and sleep difficulties. But you may need a different medication for daytime coverage. Allergy nasal sprays, such as Flonase (fluticasone), are an option to consider if you’re taking Benadryl at night.
If you’re still unsure whether Benadryl or Claritin would be better for you, ask a healthcare professional. They can help you make the best decision based on your symptoms and medical history.
How to save on Benadryl and Claritin
There are ways to save on Benadryl and Claritin, which are available as brand-name and generic medications. If a healthcare professional writes you a prescription for OTC Benadryl or Claritin, GoodRx can help you save over 80% off the average retail price.
At certain pharmacies, the price of generic Benadryl is as low as $5.05 with a free GoodRx discount. The price of generic Claritin is as low as $5.95 with a free GoodRx coupon.
The bottom line
Benadryl (diphenhydramine) and Claritin (loratadine) are popular over-the-counter antihistamines. Claritin lasts longer and is less likely to cause drowsiness than Benadryl. But Benadryl has some extra uses that Claritin doesn’t. These include treating occasional sleep troubles and motion sickness.
When used for allergy relief, Claritin tends to be a safer option for many people, especially older adults. Its lower risk of side effects makes Claritin an appealing option for all-day relief. If you’re unsure whether Benadryl or Claritin would be better for you, your healthcare team can help you decide.

Why trust our experts?


References
Bayer HealthCare. (2022). Claritin- loratadine tablet [package insert]. DailyMed.
Bayer HealthCare. (2024). Children Claritin allergy- loratadine solution [package insert]. DailyMed.
Chattem. (2023). Unisom SleepMinis nighttime sleep-aid- diphenhydramine hcl capsule [package insert]. DailyMed.
Church, D. S., et al. (2011). Pharmacology of antihistamines. World Allergy Organization Journal.
Dykewicz, M. S., et al. (2020). Rhinitis 2020: A practice parameter update. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
Kenvue Brands. (2024). Childrens Benadryl allergy- diphenhydramine hydrochloride solution [package insert]. DailyMed.
Kenvue Brands. (2024). Simply Sleep- diphenhydramine hydrochloride tablet, film coated [package insert]. DailyMed.
The Procter & Gamble Manufacturing Company. (2024). ZzzQuil Nighttime sleep-aid- diphenhydramine hydrochloride capsule, gelatin coated [package insert]. DailyMed.
Simon, F. E. R., et al. (2008). H1 antihistamines: Current status and future directions. World Allergy Organization Journal.
2023 American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria Update Expert Panel. (2023). American Geriatrics Society 2023 updated AGS Beers Criteria for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.














