GoodRx Guide
Eye Pain: Your GoodRx Guide
Comprehensive information for you or a loved one — including treatment options and discounts on popular medications.Definition
Eye pain is any type of discomfort in or around your eye. The eye is made up of many parts, and they all have to work together to let you see clearly.
You can experience eye pain when one of these parts is irritated, injured, or damaged. Eye pain is a sign that your eye is under stress from infection, injury, or inflammation.
Causes and risk factors
There are many things that can lead to eye pain. It’s impossible to list them all in one place, but some common causes are:
Eye injury: Eye injuries can happen at home or in the workplace. Some injuries are more serious than others, but they’ll all cause pain. Even seemingly minor injuries can lead to serious pain. Take corneal abrasions as an example. These painful eye injuries can be the result of very minor injuries.
Medical conditions: Some medical conditions affect the eye and cause painful inflammation of the different parts of the eye like uveitis and keratitis. Autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis often lead to eye inflammation.
Irritation around the eye: Irritation or infection of the eyelid or eyelid glands can also lead to eye pain. Common examples include chalazion and styes.
Eye surgery: Eye pain is a common side effect of eye surgery. This pain should go away quickly, but people experience pain for a least a little while afterward. Even common and safe surgeries like cataract surgery or laser eye surgery can cause pain.
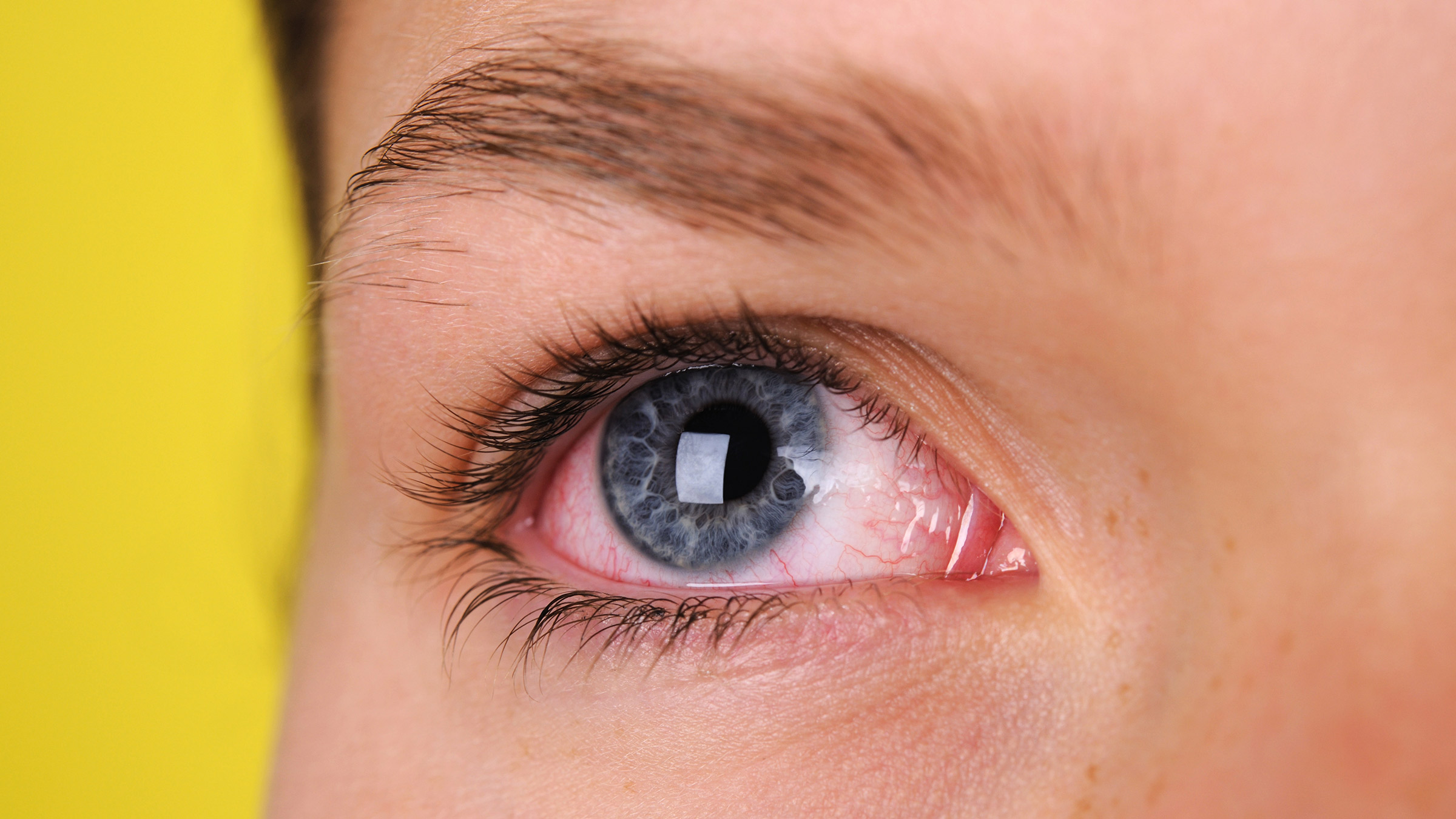
Eye infections: Eye infections can be quite painful. Even minor eye infections like pink eye (conjunctivitis) can cause pain.
Dry eye: Dry eye is a common, painful eye condition that develops when you don’t make enough quality tears.
Medications: Certain eye drops and other medications can harm the eye and lead to eye pain.
Symptoms
Eye pain can be mild or severe, depending on the cause. Some conditions lead to a sharp pain (like corneal abrasions) while others cause a deep aching pain (like iritis).
Most people with eye pain also experience other symptoms, like:
Eye irritation
Burning
Aching
Stinging
Increased tearing
Eye itching
Eyelid swelling
A feeling of something stuck in the eye

Diagnosis
Do not ignore eye pain. Eye pain is a sign that something is wrong with your eye. Many things that lead to eye pain can permanently damage your vision.
See an eye doctor as soon as possible if you have eye pain.
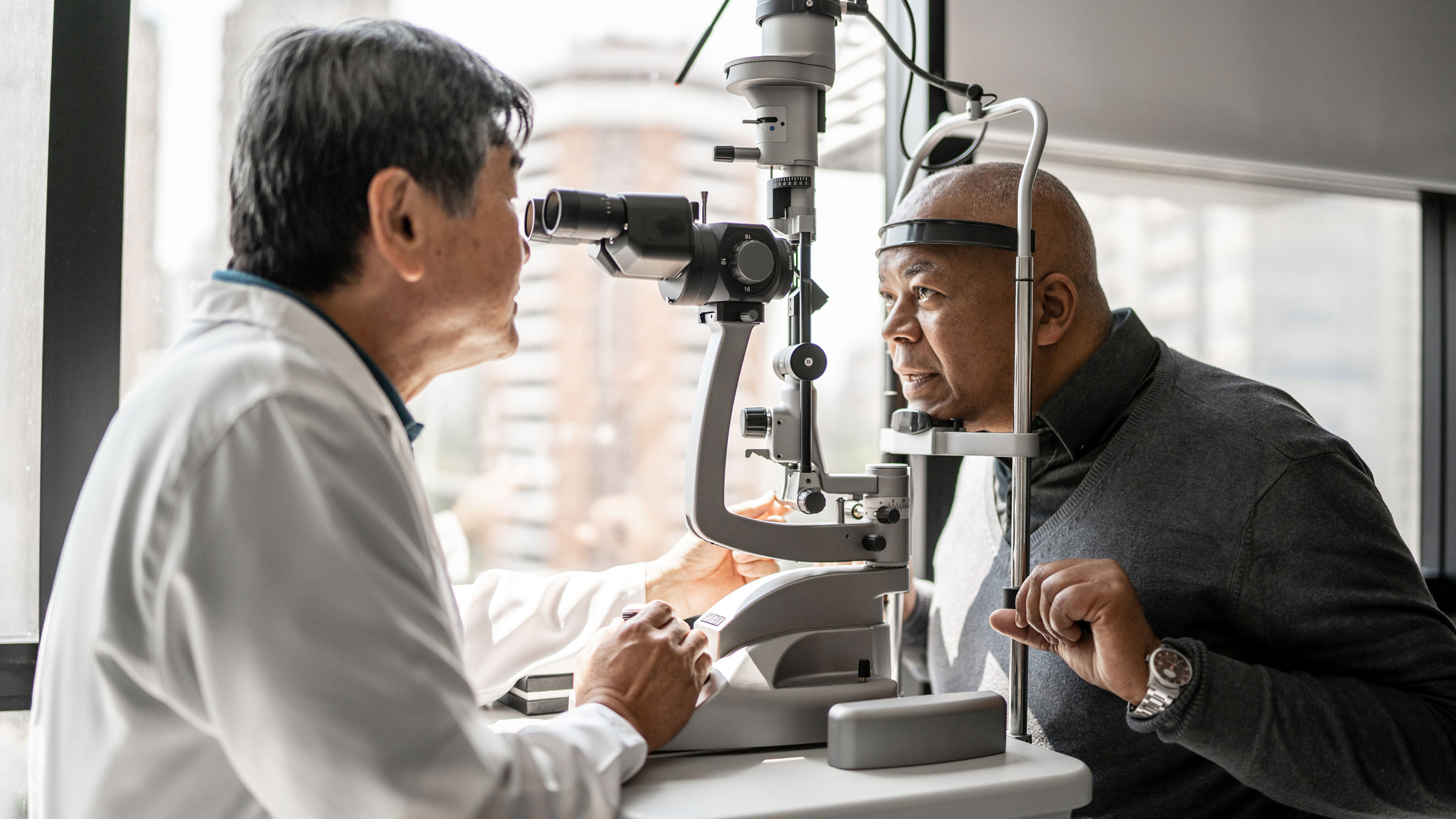
Your eye doctor will ask you about any past eye injuries, surgeries, or medical treatments. They will also perform a complete eye exam to make sure all of the parts of your eyes are healthy. This includes:
Vision check: Your eye doctor will check your vision using an eye chart to see if your vision has changed since your eye pain started.
Slit lamp exam: Using a slit lamp microscope, your eye doctor will look at the structures on the outside and inside of your eye.
Eye pressure check: Your eye doctor will check the eye pressure of both eyes to make sure this is not elevated and causing eye pain.
Dilated exam: Your eye doctor will place dilating eye drops in your eye. These drops make your pupils bigger so that your eye doctor can see the back parts of your eye, like the retina.
Treatments
Treatments for eye pain depend on the cause of the pain. Eye drops, oral medications, and eye surgery are the most common tools for treating eye conditions.
To treat what’s causing your eye pain, you may use these tools together or alone:
Eye infection: You may need oral pain medication and antibiotics along with antibiotic eye drops.
Glaucoma: You may require eye drops and laser surgery to lower the pressure inside your eye.
Eye inflammation: You may need steroid eye drops and oral pain medication.
Dry eye: You may need artificial tears, preservative-free artificial tears, lid scrubs, or immunosuppressant drops such as Restasis (cyclosporine) or Xiidra (lifitegrast).
Your eye doctor will work with you to develop a plan to treat your eye pain and the reason behind it.
Prevention
Some causes of eye pain can’t be prevented, but you can prevent others. Taking good care of your eyes will keep them healthy, safe, and pain free. These tips can prevent eye pain and keep your vision safe:
Always wear protective eye equipment if it’s recommended at your job or during your leisure activities.
Stop eye strain by using eye exercises and taking breaks while working at the computer or watching television.
Use daily lid scrubs and warm compresses if you have dry eye.
Wash your hands before removing your contact lenses, and follow the instructions from your eye doctor for storing and replacing lenses.
Common concerns
Eye pain is a sign that something is irritating your eye. Don’t ignore eye pain. If your pain doesn’t go away within a few minutes, it’s best to see an eye doctor right away.
If you notice any changes in your vision, you should also see an eye doctor right away — even if you don’t have any eye pain.
Your eye doctor will prescribe medication to help with your eye pain. And there are some things you can do at home to speed up healing. You can try over-the-counter artificial tears or a humidifier to create more moisture in your environment. And you can rest your eyes by taking breaks throughout the day. Warm or cool compresses can also provide relief for eye pain.
Stress can affect your health, and your eyes aren’t immune. Stress can cause eyelid twitching, but it shouldn’t cause vision changes or pain. If you have eye pain, don’t assume it’s from stress — see an eye doctor to make sure something else isn’t causing it.
References
Lazarus, R. (2021). 10 causes of eye pain. Optometrists Network.
MedlinePlus. (2017). Eye care.
MedlinePlus. (2021). Eye pain.
MedlinePlus. (2021). Visual acuity test.