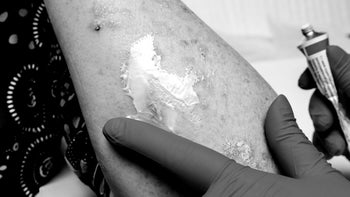
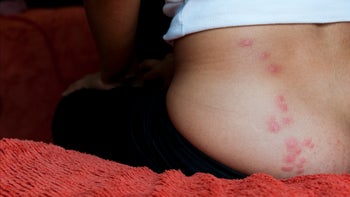
Bedbug Bites vs. Mosquito Bites: How to Tell Insect Bites Apart (With Pictures)
Key takeaways:
Bedbug bites can look similar to mosquito and other bites, but there are ways to tell them apart.
Bedbug bites tend to be in clusters, and they can sometimes form zigzags or lines. They usually happen on skin not covered in clothes at night.
Mosquito bites usually happen in a random pattern on exposed skin during the warmer summer and fall months. Flea bites are most common around the feet, ankles, and lower legs.
Table of contents

If you wake up and notice itchy bites on your skin, it’s normal to wonder if bedbugs could be the culprit. These common pests can travel from one location to another in luggage, clothing, and furniture. You may not see bedbugs, because they like to hide during the day and then come out at night to bite.
But lots of critters can cause bites. So, how do you know if you have bedbug bites, mosquito bites, or something else? Knowing what to look for can give you certain clues to the cause of your bites.
Let’s take a closer look at what bedbug bites look like to help you tell the difference between them and other bites.
Search and compare options
How to tell bedbug bites from mosquito bites
At first glance, bedbugs and mosquito bites can look similar. They both cause raised, red, itchy bumps. But there are a few clues that can help you tell them apart.
Pattern of bites
One major difference between bedbug and mosquito bites is the pattern of bites. Bedbug bites are usually grouped together in clusters of three to five bites. They can be in a straight line or zigzag pattern. This is because bedbugs usually bite more than once as they crawl across the skin. Mosquito bites tend to be isolated and scattered.
Location
Bedbugs bite at night, but they don’t bite through clothing. So they’re most likely to appear on exposed areas — like your arms, legs, and face. Mosquito bites can appear in those places as well. But they may also show up on your back or neck, since mosquitos can bite through clothing.
Timing
Mosquito bites usually cause itching and discomfort immediately. Bedbugs, on the other hand, might not cause a reaction for hours, or even days. That delayed reaction can make it hard to tell that bedbugs are causing the bites.
That said, bedbugs tend to bite overnight. So, if you wake up every morning with new clusters of bites, that’s a clue that bedbugs are playing a role.
Mosquitos are more active during dusk and dawn, especially during warmer months. So, if you come home from an evening stroll with new bites, mosquitos are the more likely culprit.
Is it hives? Sometimes bug bites and hives can look similar. See images of hives versus bug bites to learn how to spot the differences.
Found bedbugs in your home? Learn more about do-it-yourself options for getting rid of bedbugs — and when to call in the professionals.
Ease the itch: While they don’t lead to any long-term medical problems, bedbug bites are extremely itchy. Try these at-home remedies and over-the-counter options for relieving irritation.
Bedroom clues that suggest bedbugs
Other clues that can point to bedbugs aren’t your body at all. You can look for signs of bedbugs in your room. These include things like:
Small red or black stains (specks of blood) on the bedding
Tiny black dots on the bedding (bedbug droppings)
Bedbug shells (called exoskeletons) in the seams of the mattress or couch
Tiny, white oval eggs in small crevices and mattress seams
Disease transmission
Even though the idea of bedbugs might be disgusting, know that bedbugs don’t spread diseases. Mosquitos, on the other hand, can spread germs that make people sick. Through their bites, some mosquitos can transmit serious infections like:
Zika virus
Read more like this
Explore these related articles, suggested for readers like you.
What do bedbug bites look like?
Bedbug bites can look different on different skin tones:
On lighter skin tones, they usually appear like small, smooth, raised bumps.
On darker skin tones, the bumps may be harder to see. They can appear skin-colored, violet, or brown.
After the bites heal, they may leave brown marks on your skin. This is called post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, and it can take months to heal.
Pictures of bedbug bites vs. mosquito and other bites
Let’s take a look at pictures of bedbug bites and other types of bites that can look similar to them.
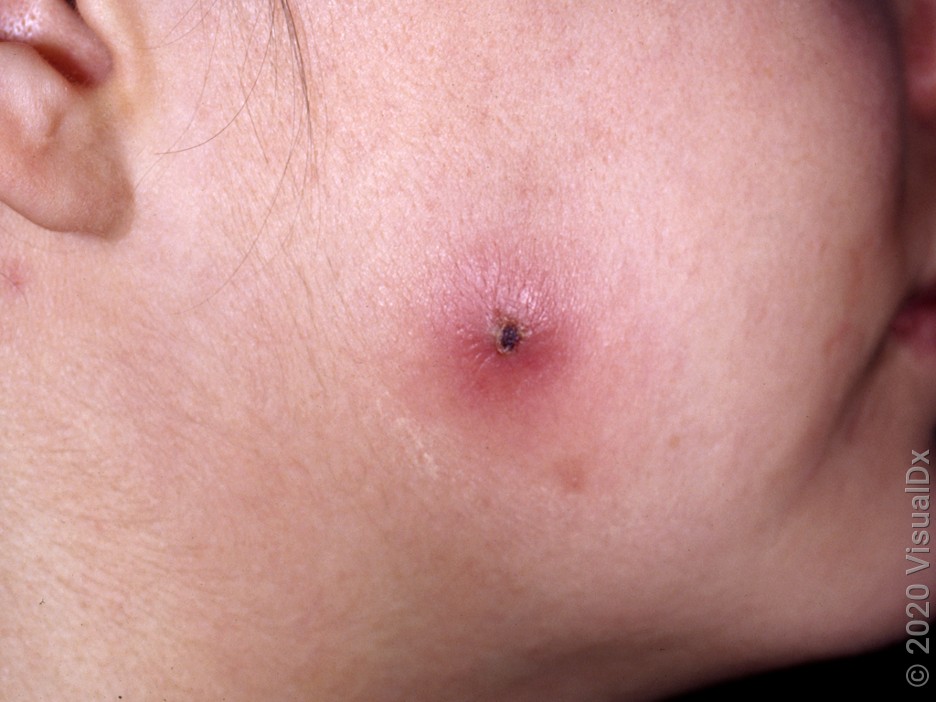
Bedbug bites
With bedbugs, some people may just have a few bites. Others may notice a dozen or more at once. Bedbug bites are usually really itchy, so they may also appear scratched or crusty.
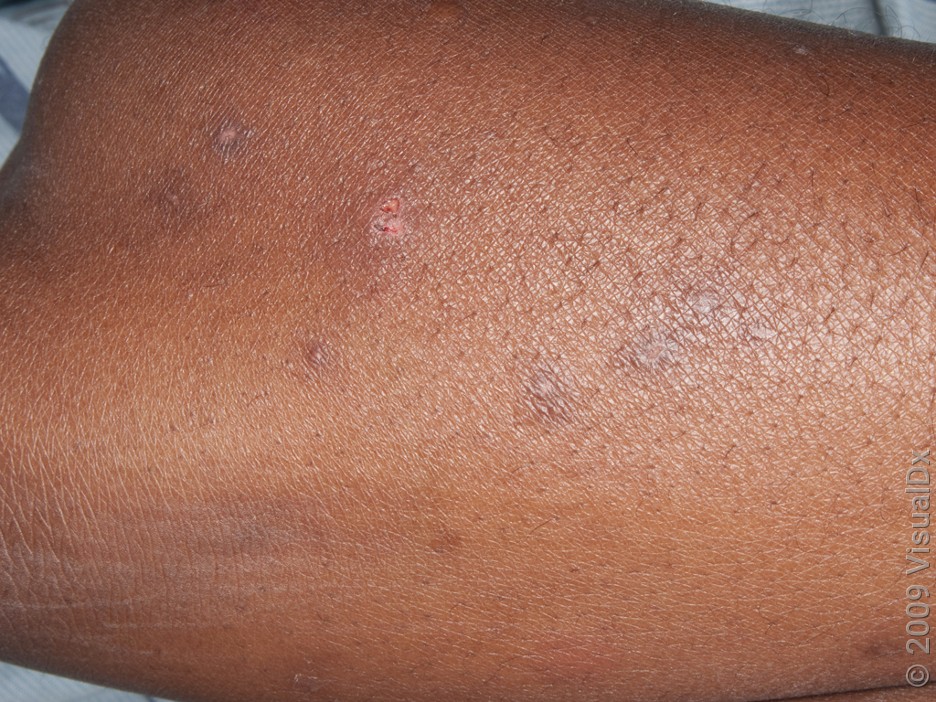
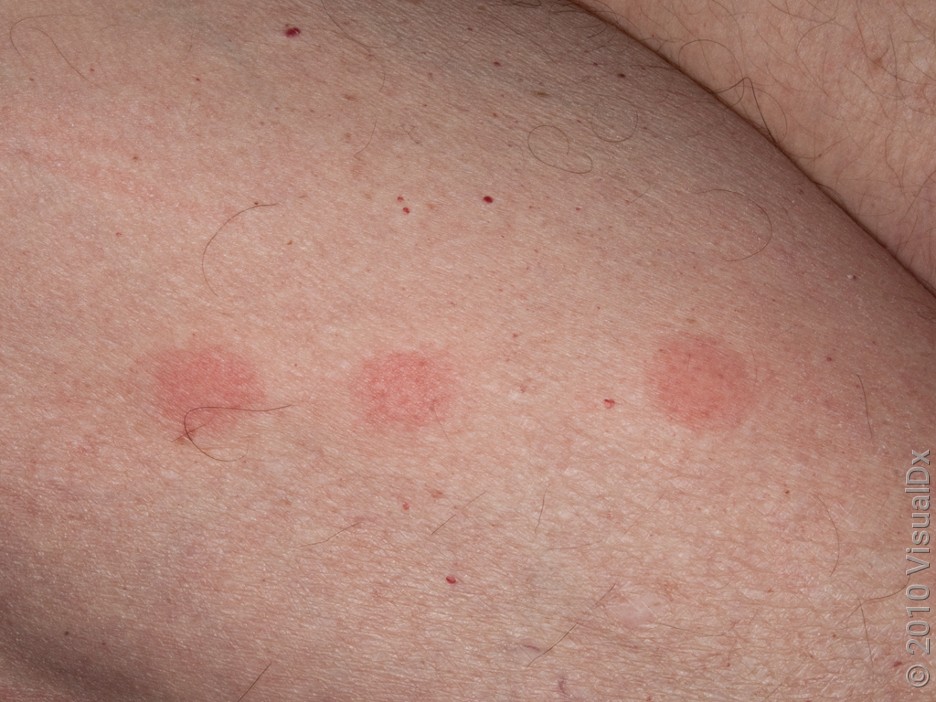
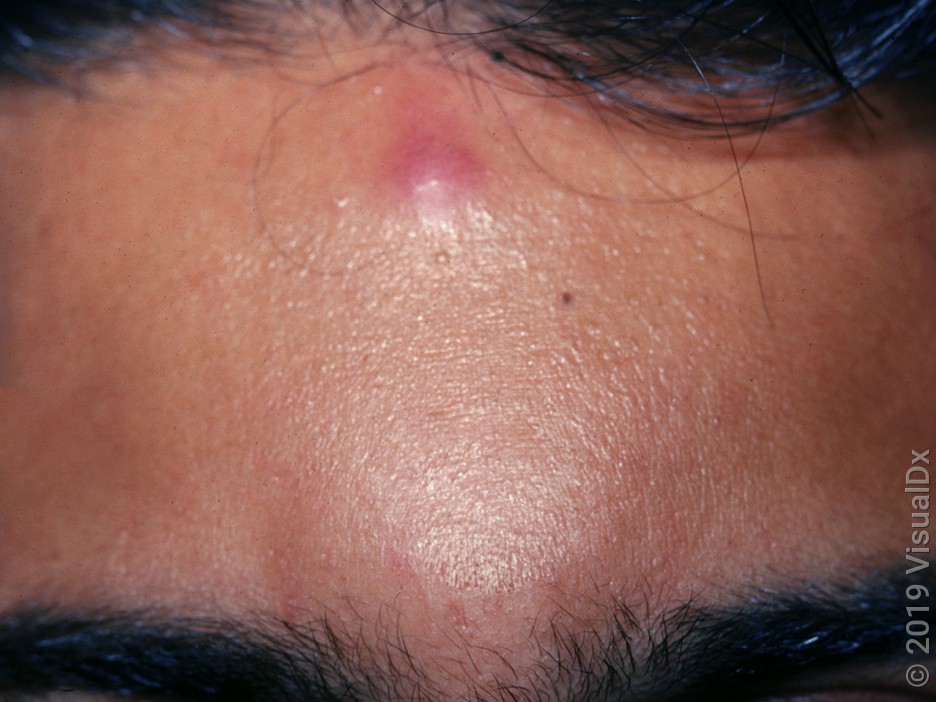
Mosquito bites
Mosquito bites can look like bedbug bites:
Smooth bumps that are red (on lighter skin)
Skin-colored, violet, or brown (on darker skin)
They also happen on uncovered skin. But unlike bedbug bites, mosquito bites usually happen in a random pattern and can be isolated.
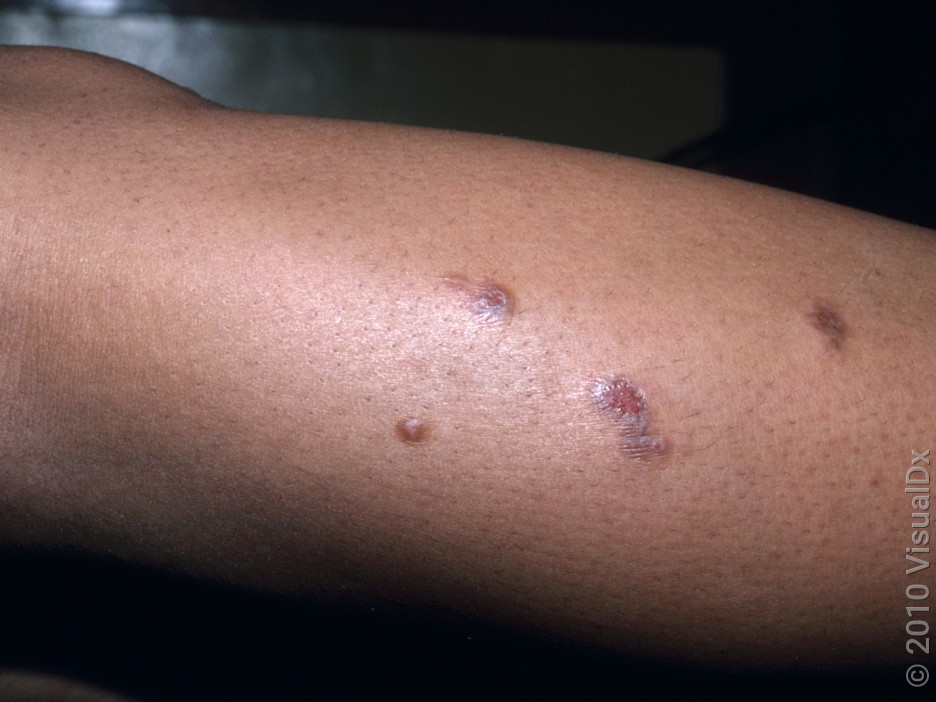
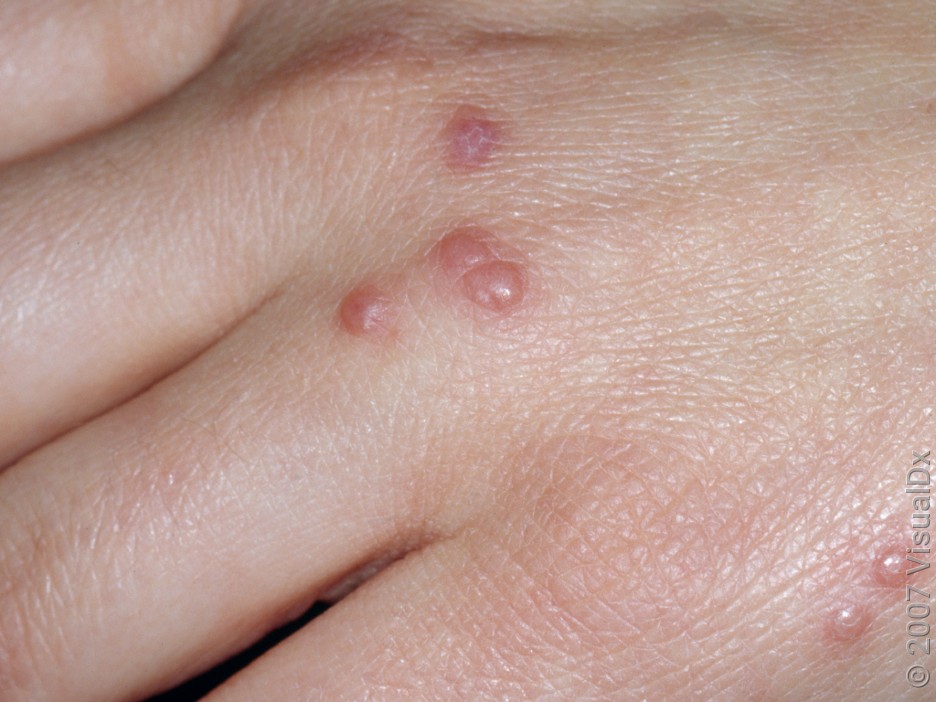
Flea bites
Flea bites form tiny skin bumps, and they’re usually around the feet, ankles, and calves. Fleas can be found in carpets after they leave a dog or cat host. From there, they can jump up to bite and feed on people. If you spend time sitting on the carpet, you may find bites on other parts of your body.
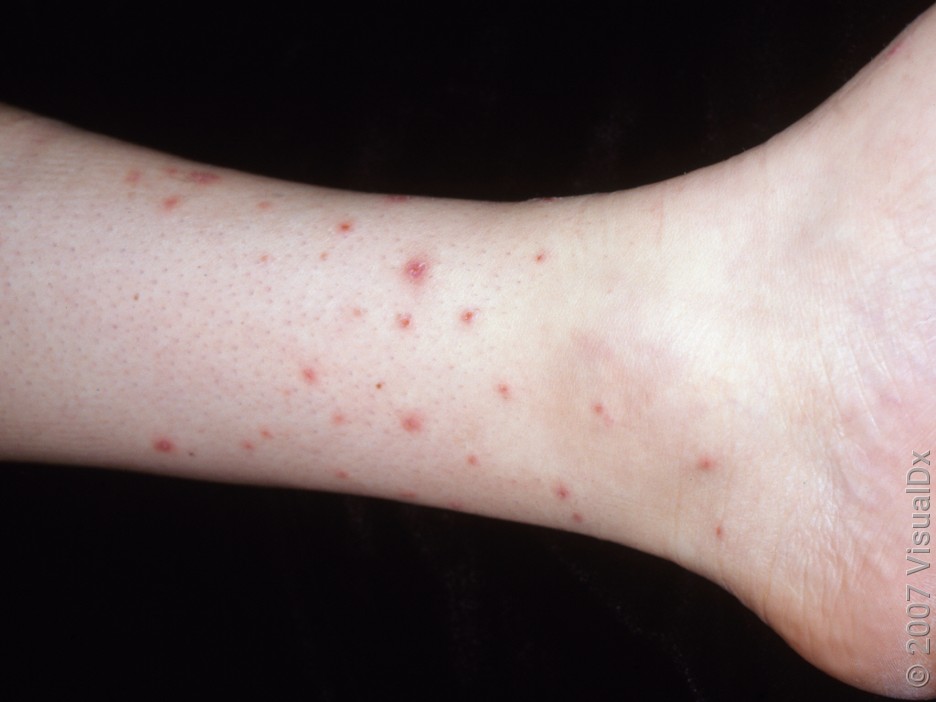
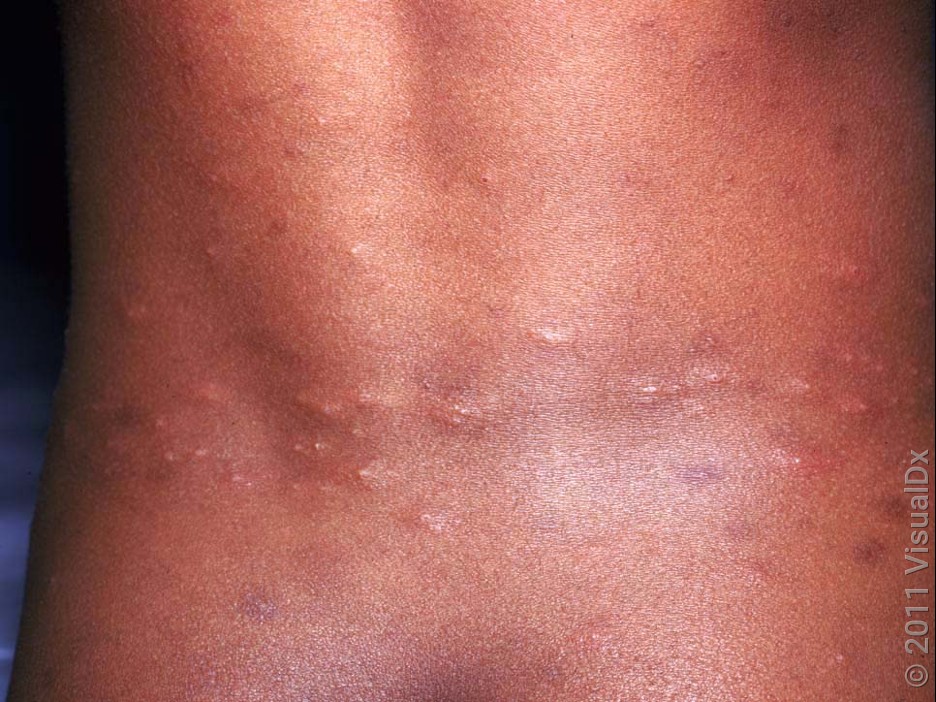
Spider bites
Spider bites are much less common than other types of bites. Unlike other insects, they usually only bite once. Mild spider bites may cause a smooth bump on the skin that’s red (on lighter skin) or violet/brown (on darker skin). The bite may have a central bite mark or crust.
More serious spider bites are pretty rare. They can cause blisters, open sores, or dark-red or brown color changes.
How to treat bedbug bites
There’s no cure for bedbug bites once you’ve been bitten. But some treatments can help minimize symptoms. Here are some options to try:
Steroid creams like over-the-counter (OTC) hydrocortisone can help relieve itchiness, swelling, and redness.
Antihistamine pills like loratadine (Claritin) can help reduce itching.
Oatmeal baths can help soothe itchy and irritated skin.
Cold compresses also help to reduce itching and swelling.
Wearing loose, breathable fabrics (like cotton) can help avoid irritating your skin even further.
And keep in mind: If you have bedbug bites, keep the area clean with soap and water. This will lower the chance of a skin infection, as scratching can break the skin and let germs enter.
How do you get rid of bedbugs?
Getting rid of bedbugs can be a challenge, especially because they’re resistant to many pesticides. Your best bet is usually to contact a pest control professional who has experience with bedbugs.
If you want to try eliminating bedbugs on your own, try these steps:
Wash your bed linens and other washable items in hot water for at least 30 minutes. Then put them in a dryer at the highest setting for at least 30 minutes.
Remove extra clutter from the room (make sure the items don’t have bedbugs before moving them into a different room).
Vacuum your mattress, your bed frame, baseboard, and furniture seams.
Enclose your bed in a mattress cover so that bedbugs can’t get in or out.
Put non-washable items in a plastic bag and then in the freezer for 3 days to kill any remaining bedbugs.
You may have to repeat these steps several times.
Frequently asked questions
Most bedbug bites will clear up in about a week. But if you haven’t taken steps to get rid of bedbugs, you can continue to get new bites for weeks or more. To help bites heal, keep the area clean and avoid scratching.
Bedbugs often bite multiple times in a night. If you see multiple red spots in a line or zigzag pattern, chances are that a single bed bug was responsible for that cluster.
The bottom line
Bedbug bites and mosquito bites may look similar, but there are helpful clues to tell them apart. Bedbug bites usually form clusters or lines, show up overnight, and target uncovered skin. Mosquito bites tend to be more scattered and appear after time outside. Signs in your bedroom — like dark stains or bedbug shells — can help confirm if you’re dealing with bedbugs. While their bites are annoying, bedbugs don’t carry disease. Still, getting rid of them can take effort and often professional help.
Why trust our experts?



Images used with permission from VisualDx (www.visualdx.com)
References
Alpert, G. D. (2009). Bed bugs. Maine.gov.
American Academy of Dermatology Association. (n.d.). Bedbugs: Diagnosis and treatment.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2024). About bed bugs.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2024). About mosquitoes in the United States.
Juckett, G. (2013). Arthropod bites. American Family Physician.
MedlinePlus. (2023). Ecthyma.
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. (2024). NIOSH fast facts: Protecting yourself from ticks and mosquitoes. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Seattle Children’s. (2025). Bed bug bite.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. (2025). Bed bugs: A public health issue.